Ladle Metallurgy Furnace Process
Ladle metallurgy furnace process was gradually developed in China in the early 1970s.
Because of its simple equipment, low investment cost, flexible operation and good refining effect,
it has become a rising star of refining equipment in the metallurgical industry and has been widely used and developed around the world.
LF ladle furnace can not only cooperate with electric furnace to replace the reduction period of electric furnace, but also cooperate with oxygen converter to produce various high-quality steel grades.
In addition, the ladle furnace is also an indispensable equipment for the continuous casting workshop, especially the alloy steel continuous casting production line to control the composition, temperature and preserve the molten steel.
Therefore, the appearance of the LF furnace has formed a new combined production line of LD-LF-RH-CC or EAC-LF-VD-CC for the production of high-quality steel.
Ladle Metallurgy Furnace Process:
Depending on the steel grade, deoxidation method and the type of primary smelting furnace, different LF furnace operating processes can be used.
The basic process of ladle refining furnace is:
The molten steel in the final stage of converter or electric furnace oxidation,
After slag removal, 50~90% of oxidizing slag is removed,
And add synthetic slag and deoxidizer in LF furnace,
In a reducing atmosphere, the desulfurization, deoxidation, alloying, temperature and inclusion control of molten steel are completed by electrode submerged arc slag making.
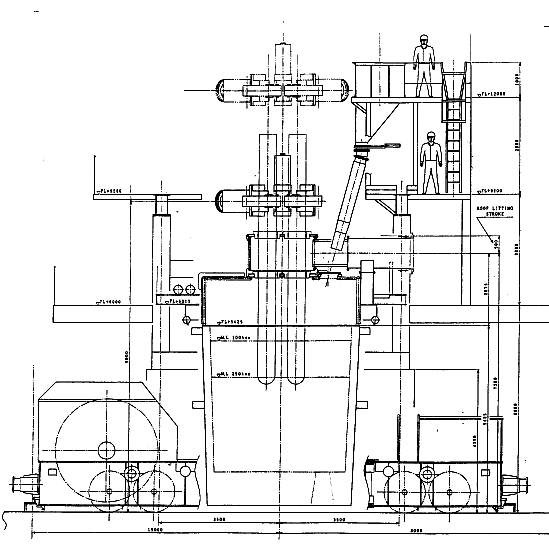
The basic principle of LF furnace refining molten steel is shown in the figure.
The LF furnace is mainly composed of a ladle equipped with a bottom blowing argon stirring device, a water-cooled furnace cover, an electrode heating system, an alloy feeding system and a dust removal device.
Under the condition of maintaining the reducing atmosphere in the ladle, the high basicity slag is heated by electric arc, and a series of slag refining such as deoxidation and desulfurization are completed while making slag.
The process can not only precisely control the chemical composition and temperature, but also have the functions of desulfurization, deoxidation and inclusion modification through synthetic slag refining.
When the LF furnace is equipped with a vacuum system, it also has a better dehydrogenation effect.
In addition, by adopting the submerged arc slag heating method, on the basis of providing the best thermal efficiency,
the strong radiation of the electrode arc to the ladle wall is effectively prevented, and the refractory part of the ladle slag line has a great protection effect. Improve the service life of LF ladle.
Ladle Metallurgy Furnace Process
Four Unique Refining Features:
①Reducing Atmosphere In The Furnace
The Ladle refining furnace itself generally does not have a vacuum system, and the refining is usually carried out at atmospheric pressure.
Mainly rely on the sealing air curtain between the ladle edge and the water-cooled furnace cover to isolate the air.
In addition, in the process of making reduced slag, the carbon in the slag and the graphite electrode during heating interact with FeO, MnO, Cr2O3 and other oxides in the slag to generate CO gas.
It increases the reducibility of the furnace gas, and maintains a slight positive pressure in the furnace, so that the oxygen content in the atmosphere of the LF furnace is reduced to about 0.5%,
which prevents the oxygen from the outside and the furnace gas from being transferred to the molten steel and ensures the refining process. reducing atmosphere in the furnace.
The molten steel is refined under reducing conditions, which can further deoxidize, desulfurize and remove non-metallic inclusions,
which is beneficial to the improvement of the quality of molten steel.
② Argon gas stirring
Good argon agitation is another feature of LF furnace refining.
Argon stirring is conducive to the chemical reaction between the steel slag.
It can accelerate the material transfer between steel and slag, which is beneficial to the deoxidation and desulfurization of molten steel. Argon blow
Stirring can also remove non-metallic inclusions, especially for the removal of Al2O3 type inclusions by floating.
It's worth mentioning that the argon-blowing stirring of the LF furnace is carried out in a reducing atmosphere that excludes the atmospheric sealing,
Therefore, the flow rate of argon blowing can be appropriately increased. Usually, after argon blowing and stirring for 15 minutes, the Al2O3 inclusions larger than 20um in the steel can be basically removed, and only small particles of Al2O3 inclusions remain in the steel.
Another function of argon stirring is to accelerate the uniformity of temperature and composition in molten steel, and to adjust complex chemical composition quickly and accurately, which is an essential requirement for high-quality steel.
③ Electrode submerged arc heating
The ladle metallurgy furnace process uses three graphite electrodes for heating.
When heating, the arc is inserted into the slag layer.
The submerged arc is used in the heating.
This method has a small radiant heat and has a great protective effect on the furnace lining.
At the same time, the thermal efficiency of heating is high, and the heat utilization rate is good. Usually, the temperature rise range can reach 3~5°C/min, which can greatly reduce the tapping temperature of the primary furnace.
At the same time, it is considered that the Ladle furnace carries out the physical heating of the electrode, which avoids the influence of a large number of A12O3 inclusions on the inherent quality of the steel produced by the heating of the RH-OB.
C and the oxides in the slag mainly react as follows:
C+FeO-→Fe+CO
C+MnO-→Mn+CO
As a result, not only the stable oxides in the slag are reduced, the reducibility of the slag is improved, but also the yield of alloying elements can be improved.
The yield of alloying elements has been greatly improved compared with the single smelting of electric furnace.
Another result of the interaction between carbon and oxides is the formation of CO gas.
The formation of CO makes the atmosphere in the LF furnace reductive, and the molten steel is refined in a reducing atmosphere, which can further improve the quality.
④White Residue Refining
The Ladle furnace is refined using white slag, which is different from other refining methods that mainly rely on vacuum degassing.
The white slag has strong reducibility in the LF furnace, which is the result of the interaction between the good reducing atmosphere and the argon stirring in the Ladle refining furnace.
The content of oxygen, sulfur and inclusions in steel can be reduced by the refining of white slag.
For more information about the ladle metallurgy furnace process and related knowledge, please feel free to pay attention to our website.
Feel free to contact us for any needs. Hani Metallurgy will provide you with the best solution as soon as possible.
E-mail: saleswn@hanrm.com / inquiry66@hanmetallurgy.com ( Daisy )


Comments
Post a Comment